Le L'écart important de compétences dans le secteur manufacturier continue de se creuser, comme le souligne une étude de Deloitte, qui a révélé que 2,1 millions d'emplois non pourvus entraîneront un coût d'environ 1500 milliards de livres sterling pour les États-Unis. en 2030 Seuls. Nous savons que le manque de talents actuel et futur s'explique par diverses raisons, principalement le vieillissement de la main-d'œuvre, les avancées technologiques qui ne permettent pas de suivre le rythme des compétences, et une vision dépassée des rôles dans l'industrie manufacturière. rappelant les conditions de travail dangereuses et peu attrayantes décrites dans « La Jungle » du romancier américain Upton Sinclair.
Selon le Chambre de commerce des États-Unis, 45 pour cent des offres d’emploi dans le secteur manufacturier restent vacantes. L'avenir de l'emploi 2023 du Forum économique mondial Un rapport souligne que 40 % des compétences requises dans le secteur de la fabrication de pointe devraient évoluer au cours des cinq prochaines années. Selon une enquête menée par l'Institut de recherche sur les technologies de l'information et de la communication (IRT), les dirigeants tirent la sonnette d'alarme. Association nationale des fabricants (NAM)Près de 75 % des directeurs d’usine ont cité la pénurie de main-d’œuvre qualifiée comme leur principal défi commercial.
Les entreprises industrielles sont confrontées à une importante pénurie de main-d'œuvre qui exige une intervention urgente. Mais comment se préparer à la crise des talents qui se profile ? Nous explorons ci-dessous les principales mesures à prendre pour responsabiliser les travailleurs grâce à des programmes ciblés de perfectionnement, garantissant ainsi résilience et croissance face aux défis de la main-d'œuvre.
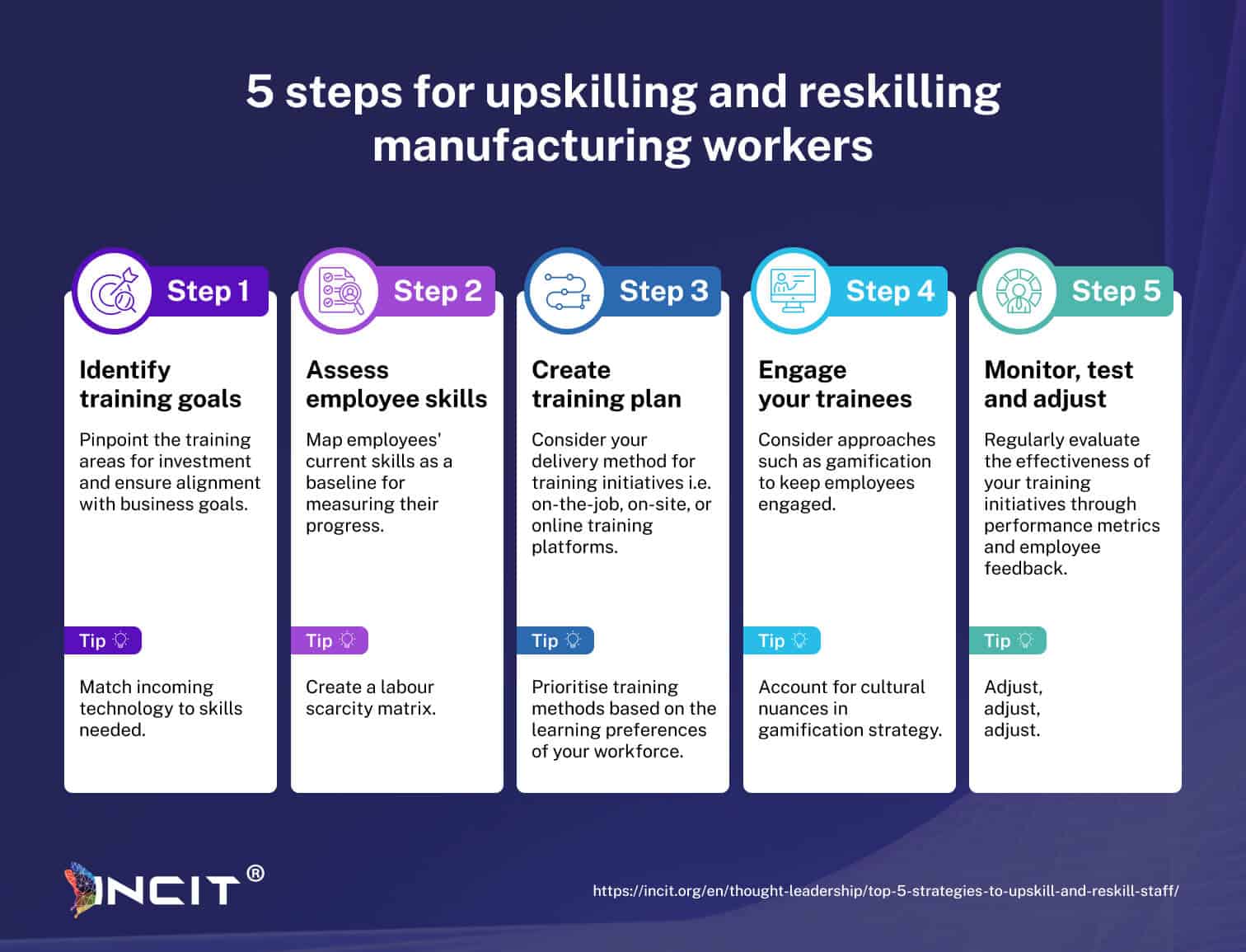
Favoriser une main-d'œuvre prête pour l'avenir grâce à des initiatives stratégiques de perfectionnement des compétences
Les pénuries de main-d'œuvre dans le secteur manufacturier sont désormais endémiques et devraient s'aggraver. Il est impératif pour les entreprises manufacturières d'investir dans des initiatives de perfectionnement et de reconversion. En mettant en œuvre des programmes de formation ciblés, adaptés à l'évolution des métiers et en exploitant des méthodes innovantes comme la gamification (à utiliser pour rendre la reconversion plus engageante !), les fabricants peuvent donner à leurs employés les moyens de s'adapter, atténuant ainsi les pénuries de main-d'œuvre. L'adoption de ces stratégies permettra non seulement de combler le déficit de compétences, mais aussi de positionner les entreprises manufacturières pour une croissance et une compétitivité durables sur le marché mondial.
De plus, des programmes de formation spécialisés, tels que le SIRI/COSIRI Programme offert par INCIT, peut accompagner les dirigeants dans le développement continu de leurs compétences grâce à cette certification, qui fait progresser la numérisation et les pratiques durables dans le secteur manufacturier. L'adoption de ces stratégies permettra non seulement de combler le déficit de compétences, mais aussi de positionner les entreprises manufacturières pour une croissance et une compétitivité durables sur le marché mondial.
Questions fréquemment posées sur le perfectionnement et la reconversion dans le secteur manufacturier
Quelles sont les 4 stratégies de perfectionnement et de reconversion ?
Les quatre stratégies clés pour le perfectionnement et la reconversion dans le secteur manufacturier sont les suivantes :
- Formation en cours d'emploi
- Plateformes d'apprentissage numérique
- Partenariats industrie-université
- Programmes de certification
Ces approches aident les travailleurs à acquérir de nouvelles compétences pour la fabrication intelligente et l’industrie 4.0.
Pourquoi la mise à niveau des compétences est-elle importante dans le secteur manufacturier ?
La mise à niveau des compétences est importante dans le secteur manufacturier car elle aide les travailleurs à s’adapter aux nouvelles technologies, à améliorer leur productivité et à rester compétitifs dans un environnement Industrie 4.0 en évolution rapide.
Quelle est la différence entre la mise à niveau et la reconversion dans le secteur manufacturier ?
La montée en compétences consiste à acquérir de nouvelles compétences pour évoluer dans un poste actuel, tandis que la reconversion consiste à former les travailleurs à des rôles entièrement nouveaux. Ces deux éléments sont essentiels dans le secteur manufacturier pour soutenir la transformation numérique et l'automatisation.
Comment les fabricants peuvent-ils créer une main-d’œuvre prête pour l’avenir ?
Les fabricants peuvent créer une main-d’œuvre prête pour l’avenir en investissant dans la formation continue, en adoptant des outils numériques, en créant des cultures d’apprentissage et en alignant le développement de la main-d’œuvre sur les technologies de l’Industrie 4.0.
Quels sont les défis auxquels les fabricants sont confrontés en matière de formation de la main-d’œuvre ?
Les fabricants sont confrontés à des défis tels que des budgets de formation limités, un manque de connaissances numériques, un personnel vieillissant et des difficultés à suivre le rythme des technologies en évolution rapide dans la fabrication intelligente.
Quels sont les exemples de perfectionnement dans la fabrication intelligente ?
Les exemples de perfectionnement des compétences dans la fabrication intelligente incluent la formation des travailleurs à l’utilisation de la robotique, des outils d’analyse de données, des jumeaux numériques, des plateformes IoT et des systèmes de production basés sur l’IA.
Comment l’industrie 4.0 affecte-t-elle la planification de la main-d’œuvre ?
L’industrie 4.0 affecte la planification de la main-d’œuvre en déplaçant la demande vers des rôles à forte technicité, en exigeant de nouvelles compétences et en poussant les fabricants à repenser les stratégies de formation, d’embauche et de rétention des talents.
Quelles sont les meilleures pratiques pour la transformation de la main-d’œuvre dans le secteur manufacturier ?
Les meilleures pratiques en matière de transformation de la main-d’œuvre comprennent des évaluations des lacunes en matière de compétences, des parcours d’apprentissage personnalisés, le développement du leadership, des partenariats avec des fournisseurs de technologie et un suivi des performances lié aux objectifs de l’Industrie 4.0.


