O a lacuna significativa de qualificação na indústria continua a aumentar, como sublinhado pela pesquisa da Deloitte, que concluiu que 2,1 milhões de empregos não preenchidos resultarão num custo de aproximadamente $1 biliões para os Estados Unidos em 2030 Sozinhos. Sabemos que existem várias razões para a atual e futura falta de talentos, resultantes principalmente do envelhecimento da força de trabalho, dos avanços tecnológicos com conjuntos de habilidades que não acompanham a evolução e de uma visão desatualizada do que é um papel na indústria. lembrando as condições de trabalho perigosas e nada glamorosas retratadas em “A Selva” do romancista americano Upton Sinclair.
De acordo com o Câmara de Comércio dos EUA, 45% das vagas de emprego no setor de manufatura continuam não preenchidas. O Futuro dos Empregos do Fórum Econômico Mundial de 2023 O relatório destaca que 40 dos atuais requisitos de qualificação na indústria de manufatura avançada devem evoluir nos próximos cinco anos. Os líderes soaram o alarme, de acordo com uma pesquisa da Associação Nacional de Fabricantes (NAM), quase 75 por cento dos gerentes de manufatura citaram a escassez de mão de obra qualificada como seu principal desafio empresarial.
Os fabricantes estão enfrentando uma escassez significativa de mão de obra que exige atenção urgente, mas o que as empresas podem fazer para se preparar para a iminente crise de talentos? A seguir, exploramos as principais medidas a serem tomadas para capacitar os trabalhadores por meio de programas de qualificação direcionados, garantindo resiliência e crescimento diante dos desafios da força de trabalho.
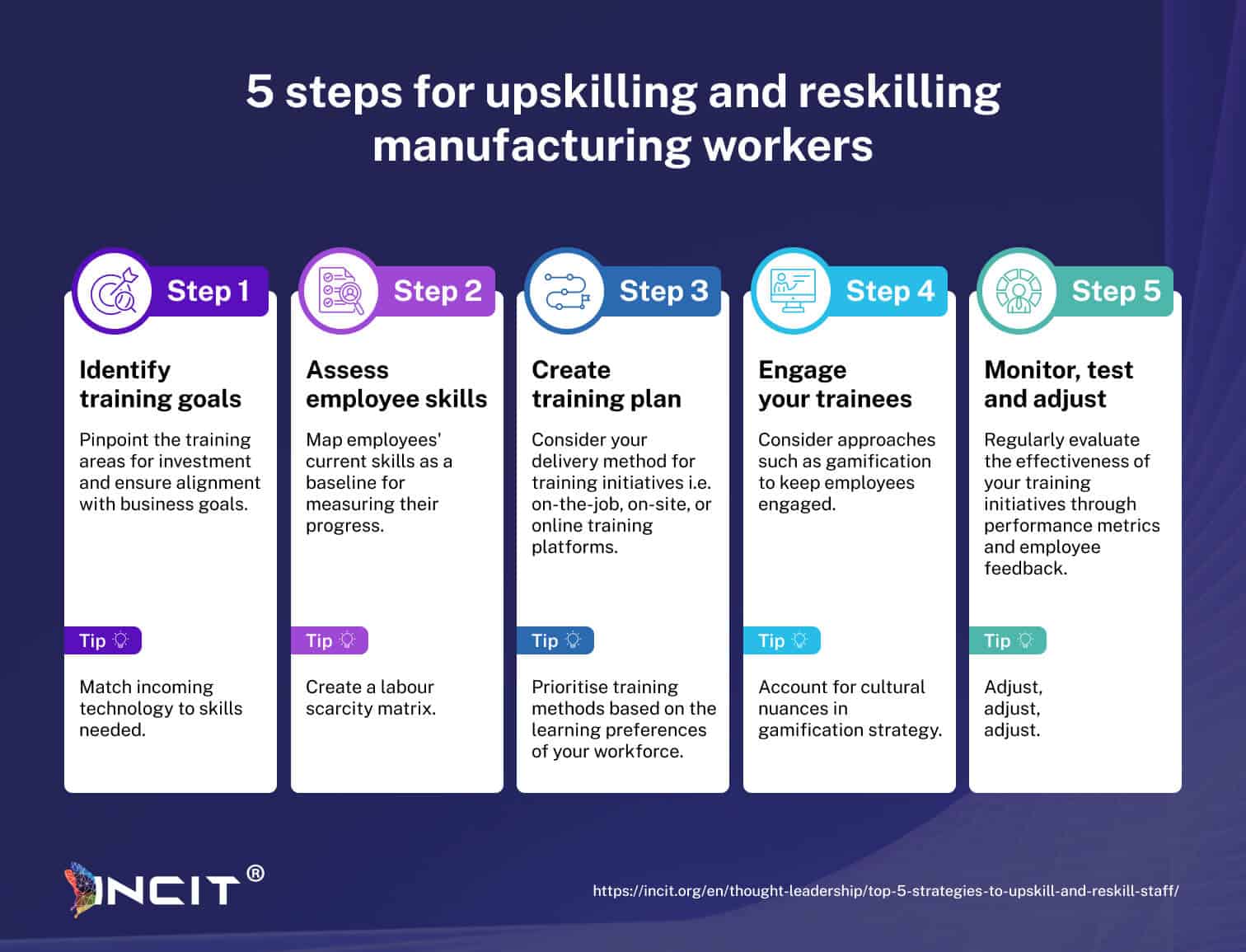
Promover forças de trabalho preparadas para o futuro por meio de iniciativas estratégicas de qualificação
A escassez de mão de obra no setor manufatureiro é endêmica e a expectativa é de que se agrave. É fundamental que as empresas de manufatura invistam em iniciativas de requalificação e qualificação profissional. Ao implementar programas de treinamento direcionados, alinhados à evolução das funções e ao aproveitamento de métodos inovadores como a gamificação (use-a para tornar a requalificação mais envolvente!), os fabricantes podem capacitar sua força de trabalho a se adaptar, aliviando assim a escassez de mão de obra na empresa. A adoção dessas estratégias não apenas reduzirá a lacuna de qualificação profissional, mas também posicionará as empresas de manufatura para um crescimento sustentável e competitividade no mercado global.
Além disso, programas de formação especializados, como o SIRI/COSIRI Programa oferecido por INCIT, pode apoiar líderes em seu desenvolvimento contínuo de habilidades com esta certificação, que promove a digitalização e as práticas de sustentabilidade na indústria. Adotar essas estratégias não apenas preencherá a lacuna de habilidades, mas também posicionará as empresas de manufatura para um crescimento sustentável e competitividade no mercado global.
Perguntas frequentes sobre requalificação e qualificação na indústria
Quais são as 4 estratégias para requalificação e atualização profissional?
As quatro principais estratégias para requalificação e qualificação na indústria são:
- Treinamento no local de trabalho
- Plataformas de aprendizagem digital
- Parcerias indústria-acadêmicas
- Programas de certificação
Essas abordagens ajudam os trabalhadores a adquirir novas habilidades para a manufatura inteligente e a Indústria 4.0.
Por que a qualificação profissional é importante na indústria?
A qualificação é importante na indústria porque ajuda os trabalhadores a se adaptarem às novas tecnologias, melhorarem a produtividade e permanecerem competitivos em um ambiente de Indústria 4.0 em rápida mudança.
Qual é a diferença entre upskilling e reskilling na indústria?
Upskilling significa aprender novas habilidades para crescer em uma função atual, enquanto requalificação envolve treinar trabalhadores para funções totalmente novas. Ambas são essenciais na indústria para apoiar a transformação digital e a automação.
Como os fabricantes podem criar uma força de trabalho preparada para o futuro?
Os fabricantes podem criar uma força de trabalho preparada para o futuro investindo em treinamento contínuo, adotando ferramentas digitais, construindo culturas de aprendizagem e alinhando o desenvolvimento da força de trabalho com as tecnologias da Indústria 4.0.
Quais são os desafios que os fabricantes enfrentam no treinamento da força de trabalho?
Os fabricantes enfrentam desafios como orçamentos limitados para treinamento, falta de conhecimento digital, envelhecimento da força de trabalho e dificuldade em acompanhar as rápidas mudanças nas tecnologias de manufatura inteligente.
Quais são exemplos de qualificação em manufatura inteligente?
Exemplos de qualificação em manufatura inteligente incluem treinamento de trabalhadores para usar robótica, ferramentas de análise de dados, gêmeos digitais, plataformas de IoT e sistemas de produção baseados em IA.
Como a Indústria 4.0 afeta o planejamento da força de trabalho?
A Indústria 4.0 afeta o planejamento da força de trabalho ao mudar a demanda para funções com conhecimento em tecnologia, exigindo novas habilidades e pressionando os fabricantes a repensar estratégias de treinamento, contratação e retenção de talentos.
Quais são as melhores práticas para a transformação da força de trabalho na manufatura?
As melhores práticas para transformação da força de trabalho incluem avaliações de lacunas de habilidades, caminhos de aprendizagem personalizados, desenvolvimento de liderança, parcerias com provedores de tecnologia e monitoramento de desempenho vinculado às metas da Indústria 4.0.


