その デロイトの調査で強調されているように、製造業におけるスキル格差は拡大し続けており、210万人の雇用が埋まらないことで米国に約1兆5千億米ドルの損失が生じることがわかった。 2030年 現在および将来の人材不足には様々な理由があることは承知していますが、主な原因は労働力の高齢化、技術の進歩に追いつかないスキルセット、そして製造業の役割に対する時代遅れの考え方です。 で描かれた危険で魅力のない労働条件を彷彿とさせる アメリカの小説家、アプトン・シンクレアの『ジャングル』。
によると、 米国商工会議所 製造業の求人のうち45%は未充足のままである。 世界経済フォーラムの2023年雇用の未来 報告書は、先進的な製造業における現在のスキル要件のうち40項目が今後5年間で進化すると予測していることを強調している。業界団体の調査によると、リーダーたちは警鐘を鳴らしている。 全米製造業協会(NAM)製造業のマネージャーの約 75% が、熟練労働者の不足を主なビジネス上の課題として挙げています。
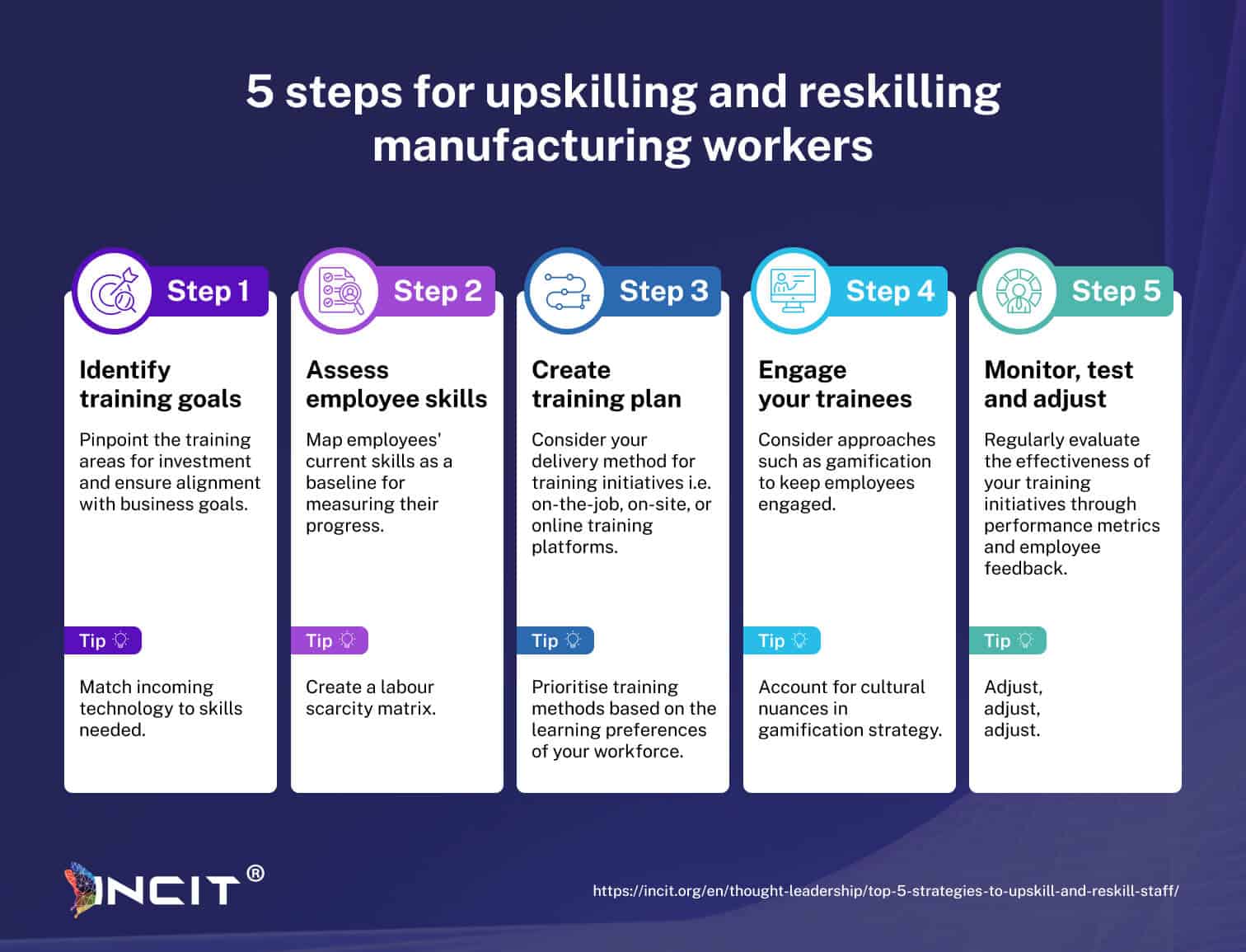
製造業は深刻な労働力不足に直面しており、早急な対応が求められています。しかし、企業は迫り来る人材危機に備えるために何ができるでしょうか?以下では、ターゲットを絞ったスキルアッププログラムを通じて従業員のエンパワーメントを図り、労働力不足という課題に直面しながらも、回復力と成長を確保するための重要なステップを探ります。
戦略的なスキルアップイニシアチブを通じて将来に備えた労働力を育成する
製造業における労働力不足は今や蔓延しており、今後さらに悪化すると予想されています。製造企業は、スキルアップとリスキリングへの投資が不可欠です。変化する職務内容に合わせた、的を絞った研修プログラムを実施し、ゲーミフィケーションなどの革新的な手法を活用することで(リスキリングをより魅力的なものにしましょう!)、製造業者は従業員の適応力を高め、ひいては企業における労働力不足を軽減することができます。これらの戦略を採用することで、スキルギャップを埋めるだけでなく、製造企業はグローバル市場における持続的な成長と競争力を確保することができます。
さらに、 シリ/コシリ プログラム 提供元 INCITは、この認定資格を通じて、製造業におけるデジタル化とサステナビリティの実践を推進するリーダーの継続的なスキル開発を支援します。これらの戦略を採用することで、スキルギャップを埋めるだけでなく、製造企業はグローバル市場における持続的な成長と競争力を確保することができます。
製造業におけるスキルアップとスキルリスキルに関するよくある質問
スキルアップとリスキリングのための 4 つの戦略とは?
製造業におけるスキルアップとスキル再習得のための 4 つの主要戦略は次のとおりです。
- 実地研修
- デジタル学習プラットフォーム
- 産学連携
- 認定プログラム
これらのアプローチは、労働者がスマート製造とインダストリー 4.0 のための新しいスキルを習得するのに役立ちます。
製造業においてスキルアップが重要な理由とは?
スキルアップは、労働者が新しいテクノロジーに適応し、生産性を向上させ、急速に変化するインダストリー 4.0 環境で競争力を維持するのに役立つため、製造業では重要です。
製造業におけるアップスキルとリスキリングの違いは何ですか?
アップスキルとは、現在の職務で成長するために新しいスキルを習得することであり、リスキリングとは、労働者を全く新しい職務に訓練することです。どちらも、製造業においてデジタルトランスフォーメーションと自動化を支えるために不可欠です。
製造業者はどのようにして未来に備えた労働力を育成できるのでしょうか?
製造業者は、継続的なトレーニングへの投資、デジタル ツールの導入、学習文化の構築、人材育成とインダストリー 4.0 テクノロジーの連携によって、将来を見据えた労働力を育成できます。
製造業者は従業員のトレーニングにおいてどのような課題に直面していますか?
製造業者は、トレーニング予算の制限、デジタルリテラシーの欠如、労働力の高齢化、スマート製造における急速に変化する技術への対応の難しさなどの課題に直面しています。
スマート製造におけるスキルアップの例は何ですか?
スマート製造におけるスキルアップの例としては、ロボット工学、データ分析ツール、デジタルツイン、IoT プラットフォーム、AI ベースの生産システムを使用するための労働者のトレーニングなどがあります。
インダストリー 4.0 は人材計画にどのような影響を与えますか?
インダストリー 4.0 は、技術に精通した役割への需要の移行、新しいスキルの要求、メーカーによるトレーニング、雇用、人材維持戦略の見直しを促すことで、人材計画に影響を与えます。
製造業における労働力変革のベストプラクティスは何ですか?
人材変革のベストプラクティスには、スキルギャップ評価、パーソナライズされた学習パス、リーダーシップ開発、技術プロバイダーとのパートナーシップ、インダストリー 4.0 の目標に結びついたパフォーマンス追跡などがあります。


